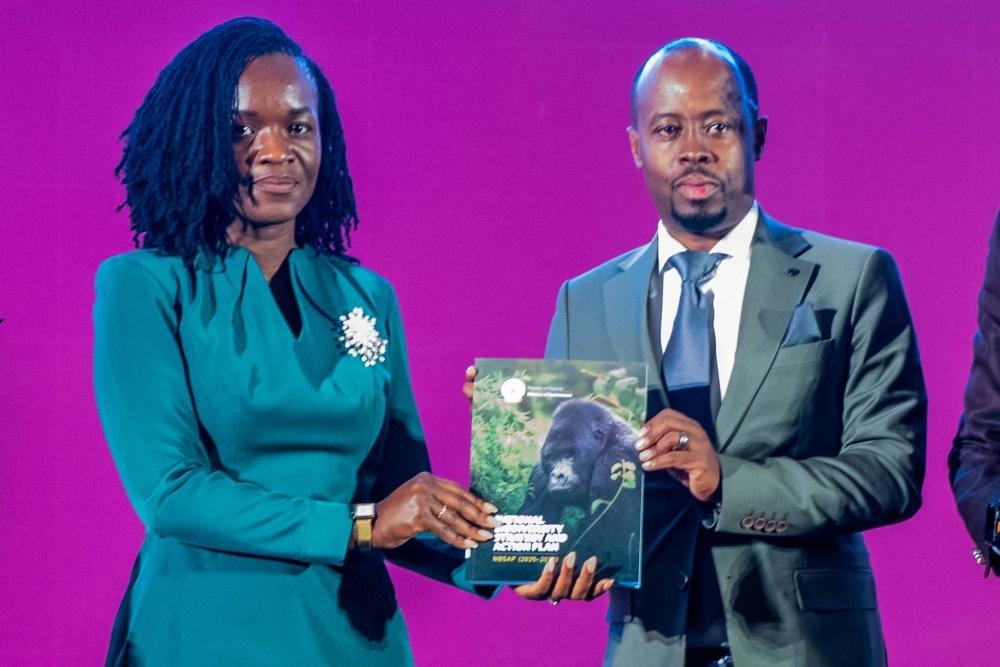
Africa-Press – Rwanda. The government has launched a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP), expected to cost Rwf399.8 billion from 2025 to 2030.
Developed under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the plan complies with Article 6, according to Juliet Kabera, Director General of the Rwanda Environment Management Authority (REMA).
The CBD is an international treaty adopted in 1992 at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
In 2022, the convention parties adopted the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), setting targets for 2030, including protecting 30% of the planet’s land and oceans.
Participants follow Minister of Environment, Bernadette Arakwiye’s remarks at the launch.
“Rwanda continues to advance its commitments under the CBD. Article 6 requires countries to develop National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans and integrate biodiversity conservation into national policies,” Kabera said.
Rwanda’s 2025–2030 strategy outlines 22 national targets, integrated across sectors.
Here are 22 national targets
1. Close to zero biodiversity loss
By 2030, land use planning and management will ensure biodiversity loss is close to zero.
2. Restore degraded lands, inland waters by 10%
The government will restore degraded lands and inland waters by at least 10% by 2030. The Climate, Environment and Natural Resources Sector Strategic Plan (2024–2029) aims to increase restored area from 332,861 ha to 600,000 ha.
3. Conservation of terrestrial and inland water areas
By 2030, 11% of land and inland water areas will be conserved through protected areas. Protected areas currently cover 9.1% of Rwanda.
4. Halting the extinction of threatened species
Conservation efforts will be enhanced to improve biodiversity, halt species extinction, and manage human-wildlife conflict.
5. Curb illegal harvesting of wild species
Rwanda will sustainably manage wild species on all lands and eliminate illegal harvesting.
6. Controlling invasive alien species by 50%
Invasive alien species will be reduced by 50% in protected areas by 2030. A 2016 REMA study identified 47 such species in Rwanda.
7. Reduce major pollutants from agriculture
Pollutants from agriculture, industry, and mining will be reduced to non-harmful levels for biodiversity through efficient nutrient cycling and reduced pesticide use.
8. Minimise the impacts of climate change on biodiversity
The strategy will build resilience to climate change through expanded nature-based and ecosystem-based solutions in vulnerable areas.
9. Sustainable management and use of wild species
Wild species will be managed sustainably to protect biodiversity and benefit communities.
10. Management of areas under agriculture, aquaculture, fisheries, and forestry
Agriculture, aquaculture, fisheries, and forestry areas will adopt biodiversity-friendly practices. Conservation agriculture will expand by 22,000 ha as per PSTA 5.
11. Ecosystem services
Ecosystem services will be restored and enhanced through nature-based solutions to improve human well-being and sustainability.
12. Improving urban green spaces
Urban planning will increase green spaces using native species, supporting biodiversity and urban well-being.
13. Benefits arising from the utilisation of genetic resources
Legal frameworks will ensure fair benefit-sharing from the use of genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
14. Integration in policies, laws
Biodiversity values will be integrated into laws, regulations, plans, and decision-making across all sectors.
15. Financial institutions’ role
Large businesses and financial institutions in Rwanda will assess, disclose, and reduce biodiversity-related risks and impacts.
16. Reducing waste
Sectors will implement sustainable production and consumption strategies to reduce waste and overconsumption.
17. Biosafety measures in place
Capacity will be strengthened for biosafety and sustainable use of biotechnology products and services.
18. Identify possible harmful incentives and subsidies
Harmful incentives that damage biodiversity will be identified, while positive incentives will be promoted.
19. $500m to be mobilised
Rwanda will mobilise $500 million from public and private sources and align financial flows with biodiversity goals.
20. Technology transfer
Capacity-building, technology transfer, research, and communication will be enhanced to support biodiversity efforts.
21. Data
Biodiversity data will be made accessible and used to guide conservation and sustainable use.
22. Women, youth, and persons with disabilities involved
All stakeholders, including women, youth, and persons with disabilities, will participate in biodiversity-related decision-making, respecting traditional knowledge.
Economic valuation of biodiversity and ecosystem services
The strategy is based on the economic valuation of biodiversity and ecosystem services in protected areas, showing significant national benefits.
Nyungwe National Park was valued at $4.8 billion in 2014. Rugezi Wetlands had a Total Monetary Value of $374 million, while the Mukura Landscape was estimated at $1.4 million annually.
An assessment of the Akagera Wetland Complex found annual benefits of $12 million and a carbon storage stock value of $1.1 billion.
The Kigali City Wetlands Complex provides $22 million annually in provisioning services and $499,000 in regulating services. Tourism and recreation in this complex have an estimated annual value of $83,333.
One of biodiversity’s largest contributions to Rwanda’s economy is through ecotourism. Tourism remains a key sector for sustainable development and income generation.
For More News And Analysis About Rwanda Follow Africa-Press